Electronic Invoice or E-invoicing under Goods and Service Tax (“GST”) is in discussion since long time and GST Council has decided to implement e-invoicing system in a phased manner with effect from 1st January, 2020 on Voluntary Basis. However e-invoicing under GST is made mandatory for tax payer having turnover of more than 500 cr in preceding Financial year with effect from 1st October 2020 and later the tax payer with turnover 50 cr need to generate mandatory einvoicing from 1st April 2021 onwards.
Read more on Procedure of E-Invoice Generation under GST | Brief User Manual
In this article we have made an attempt to discuss concept of electronic invoice in detail and we will cover various topics such as what is the need of electronic invoice? What is the process of generation of electronic invoice? Benefits of e-invoicing mechanism, etc.
One may come up with a question that what is the requirement to have electronic invoicing in place? Invoices are core documents of Indirect taxes from very beginning and need of electronic invoice have never felt before.
- Presently, taxpayer uses different software for generation of invoice such as SAP, Tally, Buzy etc. and invoice generated by one system may not be read by another system.
- For inter-operability of e-invoices across the entire GST eco-system, it is mandatory to have standards to eliminate the need of fresh data entry.
- Machine readability and uniform interpretation of document is the key objective of e-invoicing.
- Apart from GST, adoption of standards will make sure that invoice shared by supplier with his buyer and bank or agent or any other person can be read by machine.
- Therefore, GST council in its 37th GST Council meeting held on 20th September, 2019 has approved standards for generation of e-invoice.
2. What is e-invoice?
- Myth:
- About e-invoicing, there are lot of myths taxpayers have in their mind such as generation of invoice through software on computer or Point of Sales {“PoS”) machine is an electronic invoice or
- e-invoice means generation of invoice from central portal of tax department.
This is not the case. Generation of invoice from a central portal will create a lot of restriction for trade.
- E-invoicing is about adoption of standards for preparation of invoice which will standardize the format in which electronic data of invoice will be shared with the others to ensure inter-operability of data.
- Standards will not impact the physical appearance of invoice. Contrary, all the software will adopt the new e-invoice standards wherein they will re-align their data access and retrieval in standard format.
- As a taxpayer, user will not be required to take any action. They will only be required to update their software versions to sync such changes in their system.
- For small taxpayers, GSTN has empanelled 8 accounting and billing software which will provide basic accounting and billing system free of cost to small taxpayers. Such software will be available in online mode (i.e., cloud based) and offline mode (i.e., install on computer system of the user)..
3. How does e-invoicing works?
- Generation of e-invoice will be the responsibility of taxpayer who will be required to report the invoice to Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) of GST which in turn will provide a unique Invoice Reference Number (“IRN”), will digitally sign it and also allocate a QR code.
- QR code will contain vital parameters of the e-invoice and will return the same to the taxpayer who generated it.
- Process of e-invoicing contains 2 major steps:
- The first part being the interaction between the business (supplier in case of invoice) and The Invoice registration Portal;
- Second part is the interaction between the IRP and GST/E-waybill systems and the buyer.
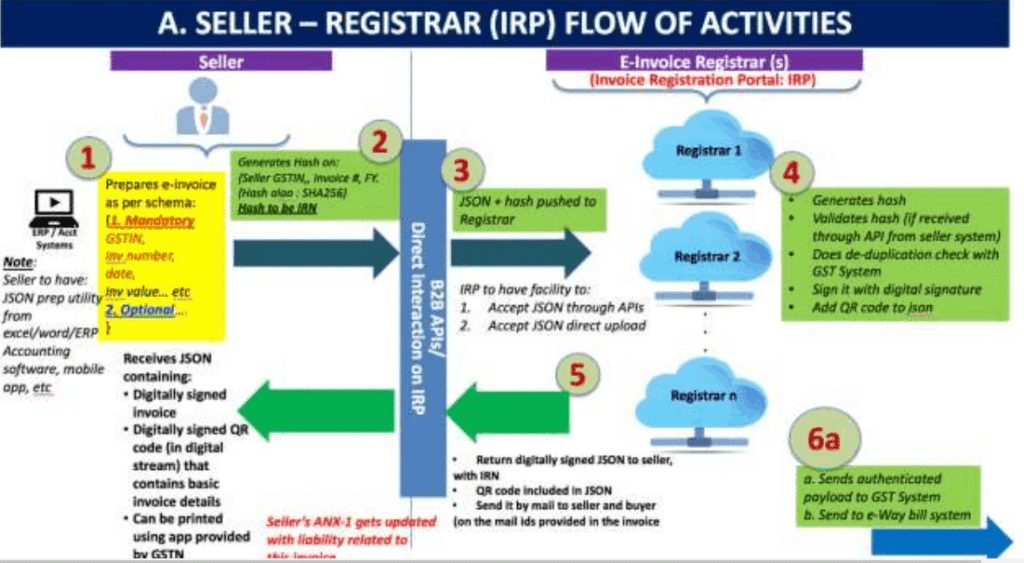
Step-1: Flow of information from supplier to IRP
- Supplier shall generate the invoice in his own accounting and billing software which contains all the standards notified for invoice generation. Then, Supplier’s software must be capable of generating a JSON of the final invoice or supplier can extract details of invoices in excel format and then can enter the data in “Bulk Generation Tool” provided by GSTN itself to generate JSON File that can be uploaded on IRP. Only JSON files can be uploaded on IRP.
- Click here to read about process of generation of e-invoice| User Manual
- Supplier shall generate a unique Invoice reference number (“IRN”) (known as “Hash” in technical term). This is an optional step. Supplier can generate IRN and upload it alongwith Invoice data. IRN shall be based on 3 parameters namely:
- GSTIN of supplier
- Invoice Number
- Financial year to which invoice pertains
- Supplier shall upload the JSON generated of final invoice alongwith IRN, if generated. Uploading can be done directly on IRP or through GSPs or through third party provided applications.
- IRP shall validate the hasp uploaded by supplier alongwith JSON file or will generate the hash if it not already generated.
- IRP shall check the hash from the Central Registry of GST system to make sure that same invoice pertaining to same supplier for same Financial year is not uploaded again.
- Upon validation form central registry, IRP shall add its digital signature to JSON file and also will add QR code to the JSON file. The QR code will contain GSTIN of seller and buyer, Invoice number, invoice date, number of line items, HSN of major commodity contained in the invoice as per value, hash etc.
- The hash computed by IRP will become the IRN (Invoice Reference Number) of the e-invoice. IRN shall be a unique number for each invoice for entire financial year.
- Then step 2 will start with sharing of data with GST and e-waybill system.
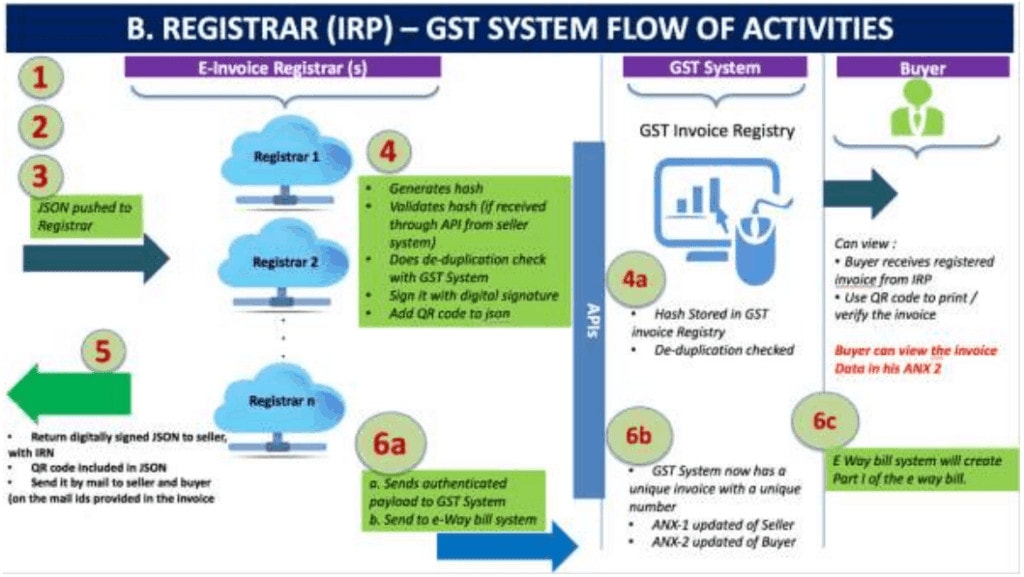
Step:2 Flow from IRP to GST System/e-waybill system & buyer
- IRP shall share the signed copy of e-invoice data alongwith IRN, QR code and digital signature to the GST system as well as e-waybill portal.
- Using such shared information, GST system shall update the ANX-1 of supplier and ANX-2 of buyer, which in turn shall determine the liability and ITC.
- E-waybill system shall generate the part-A of e-waybill using such data and supplier/buyer will be required to update only Vehicle number in Part-B.
Notes:
- E-invoicing standards shall contain some mandatory information and some option items. System shall not accept the electronic invoice unless all the mandatory information is available. Optional information may be used by supplier as per their business requirements.
- Supplier may send his data for registration of invoices to more than one registrar. However, IRP shall carry out a de-duplication check and will make sure that only one IRN is allotted to a invoice. Therefore, is same invoice is uploaded at multiple IRPs then system will generate only one IRN and will reject other requests.
- QR code shall enable a quick review, validation and access of the invoices from the GST system.
4. What are the benefits of E-invoicing?
- This concept makes e-invoices completely inter-operable eliminating transcription and other errors.
- It provides better taxpayer service as upon uploading electronic invoice, system will automatically update ANX-1, ANX-2 and part-A of e-waybill. It will reduce the duplication of efforts and will also automate the process of reconciliation.
- Complete trail of B2B invoices will reduce possibility of tax evasion.
- Elimination of fake invoices will increase efficiency of tax administration.
5. Turnover Limits for Einvoicing.
E-invoice has been implemented in a staggered manner based on aggregate turnover of person. Following is the date of applicability of e-invoice on different class of taxpayers:
| Class of taxpayer | Date of applicability of e-invoice provisions | Legal reference |
| With aggregate turnover of more than INR 500 crores during any preceding Financial year from 2017-18 onwards* | 1st October, 2020 | NOTIFICATION No. 61/2020–Central Tax dated 30-07-2020 |
| With aggregate turnover of more than INR 100 crores during any preceding Financial year from 2017-18 onwards | 1st January, 2021 | NOTIFICATION NO. 88/2020–Central Tax dated 10-11-2020 |
| With aggregate turnover of more than INR 50 crores during any preceding Financial year from 2017-18 onwards | 1st April, 2021 | NOTIFICATION NO. 05/2021–Central Tax dated 08-03-2021 |
* Earlier, e-invoice was made applicable based on aggregate turnover in Financial year. However, vide Notification No. 70/2020-Central Tax dated 30.09.2020, aggregate turnover was to be considered for any preceding financial year from 2017-18 onwards.
6. Which Class of persons are exempted from generation of e-invoice?
As per Notification No. 13/2020-Central Tax dated 21st March, 2020, following class of persons are not required to generate e-invoice irrespective of their turnovers:
- Special Economic Zone Unit
- Insurance Company, Banking Company, Financial Institutions and Non-Banking Financial institutions
- Goods transport agencies
- Person providing passenger transport services
- Person providing service of admission to exhibition of cinematograph films in multiplex screens
7. What type of documents is required to be reported to GST System?
As per Notification No. 13/2020-Central tax dated 21st March, 2020, eligible persons should generate e-invoice with for every supply of goods or services or both to registered persons or for export. Therefore, E-invoicing is required for following documents:
- Tax Invoice issued to registered person
- Credit Note by supplier issued to registered person
- Debit note by supplier to registered person
- Invoice issued for export of goods or services (with or without payment of GST)
- Invoice issued for supply of goods or services to Special Economic Zone (with or without payment of GST)
- Invoice issued for deemed export
- Any other document as required for supply of goods or services to registered persons.
8. Whether any uploading is required for B2C transactions?
As per notification no. 14/2020- Central Tax dated 21st March, 2020, In case of supply of goods to unregistered person by the person whose turnover exceeds INR 500 crores during any preceding Financial year from 2017-18 onwards then such person is required to generate QR Code for such B2C Invoice.
Such QR code is not generated through e-invoicing portal rather same is generated by supplier himself. Further, if supplier provides any other QR code for payment purpose, such as QR code for payment through paytm or UPI, then such QR code shall be considered as valid for GST purpose. However, If payment is made after some time of generation of Invoice then QR code generated for payment shall not be considered as valid and supplier will be required to create a separate QR Code for such invoice.
9. Direct generation of invoice on Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)
Some people are of the opinion that e-invoicing shall facilitate the generation of invoice on government’s tax portal. This is a myth and taxpayer shall continue to generate invoice from their respective accounting software. However, small taxpayer may use one of the eight emplaned software to generate invoices.
10. What will be the format of Unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN)?
- The unique IRN will be based on GSTIN of generator of document (invoice or credit note etc.), Year and Document number like invoice number. The hash could also be generated by the taxpayers based on above algorithm.
- Accordingly, one can pre-generate and print hash on the invoice book, however, the same will not make the invoice valid unless it is registered on the portal along with invoice details.
- Further, The hash algorithm that is to be used by the taxpayers has been specified in the e-invoice standard that is published. The hash will be the IRN.
- To ensure duplication check, the registrar will be required to send the hash to Central Registry of GST System to confirm whether the same has been reported already. In case it has been reported by another registrar and the Central Registry already has the same IRN, then the registrar will reject the registration and inform the sender. Only unique invoices from a taxpayer will be accepted and registered by the registrar.
11. What is the use of Digital Signing by e-Invoice Registration Portal?
- IRP (Invoice Registration Portal) shall generate a hash to verify the invoice or use the hash submitted with invoice data and then will digitally sign such invoice with the private key of the IRP.
- The IRP will sign the e-invoice along with hash and the e-invoice signed by the IRP will be a valid e-invoice and used by GST/E-Way bill system.
12. What is the use of QR Code on electronic invoice?
- The IRP shall generate a QR code containing the unique IRN (hash) along with some important parameters of invoice and digital signature so that it can be verified on the central portal as well as by an Offline App.
- This will be helpful for tax officers to check the invoice on the roadside where Internet may not be available all the time.
- The QR code will consist of the following
e-invoice parameters:
- GSTIN of supplier
- GSTIN of Recipient
- Invoice number as given by Supplier
- Date of generation of invoice
- Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
- Number of line items.
- HSN Code of main item (the line item having highest taxable value)
- Unique Invoice Reference Number (hash)
13. How verification of the invoice will be done through QR Code?
- An offline app will be provided on the IRP to authenticate the QR code of the invoice offline and its basic details. However, to see the whole invoice, one will have to connect to the portal and verify and see the details online.
- The facility to download entire invoice will be provided to tax officers, the way it is currently available under E-way bill system.
- The facility of QR code verification will be made available only through GST System and not IRP. This is because the IRP shall store the invoice for next 24 hours only. In order to achieve speed and efficiency, the IRP will be a lean and focused portal for providing invoice registration and verification service, IRN and the QR codes. Hence, storing of the invoices will not be a feature of the IRP.
14. What is the Difference between QR Code affix on B2B Invoices and B2C invoices?
- QR Code on B2B invoices is generated by e-invoice portal alongwith IRN and digital signature. Therefore, same can be verified through QR code scanning app provided by GSTN. Through scanning QR Code, app will verify that whether QR Code is valid or not.
- However, QR Code on B2C invoices are generated by supplier himself and same can’t be verified through app provided by GSTN. Purpose of enabling QR Code on B2C invoices is to promote digital payment.
15. Frequently asked questions on e-invoice
15.1 What is the time limit of generation of e-invoice?
As such there is no time limit is given under GST law for generation of e-invoice. Further, no validation is also created on e-invoice portal for document date.
However, as per Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, all eligible class of persons are required to upload detail of invoices on e-invoice portal and invoice shall be issued after generating an Invoice reference number. Any invoice issued without IRN shall be considered as invalid.
E.g.
| Date of generation of Invoice | Date of Generation of IRN | Date of supply of goods | Legal status |
| 1st March, 2021 | 1st March, 2021 | 1st March, 2021 | Such movement of goods shall be considered as valid as goods are moved under a valid tax invoice, i.e, Invoice with IRN |
| 1st March, 2021 | 2nd March, 2021 | 1st March, 2021 | Even though e-invoice portal shall not restrict the generation of e-invoice on 2nd March, 2021. However, when goods are moved on 1st March, 2021 with a invalid invoice then such movement shall be considered as without invoice and goods can be detained for such non-compliance. |
15.2 Whether persons with aggregate turnover of less than INR 50 Crores can create e-invoice on optional basis?
No. Facility to generate e-invoice is available for persons aggregate turnover of more than INR 50 Crores. E-invoice portal shall allow to create login credentials to such person whose aggregate turnover exceeds INR 50 crore in GST returns. However, if portal doesn’t allow to create login credentials then supplier is required to enable e-invoice facility against his GSTIN. While enabling e-invoicing, declaration is required to be given that aggregate turnover of supplier exceeded INR 50 crores during any of the preceding year from 2017-18 onwards.
15.3 whether persons selling through e-commerce platform is required to generate e-invoice?
If aggregate turnover of any seller exceeds INR 50 crores during any of the preceding year from 2017-18 onwards then he is required to generate e-invoice. No specific exemptions are given for persons selling through e-commerce operator. Therefore, they are required to generate e-invoice if above mentioned condition are fulfiled.
15.4 Similar to waybill, Whether recipient can generate e-invoice instead of supplier?
No. Only supplier can generate e-invoice.
15.5 Whether e-invoice is applicable on supplies covered under RCM?
Yes. If supplier is registered under GST and supplying any goods or services which covered under RCM and condition of aggregate turnover is satisfied then supplier is required to generate e-invoice. However, if recipient is generating self-invoice for transactions liable to RCM then no e-invoice is required.
15.6 Which year is to be considered for checking aggregate turnover of INR 50 Crores of preceding year?
Each year from F.Y. 2017-18 onwards are to be considered. If aggregate turnover during any year exceed INR 50 crores then supplier is required to generate e-invoice.